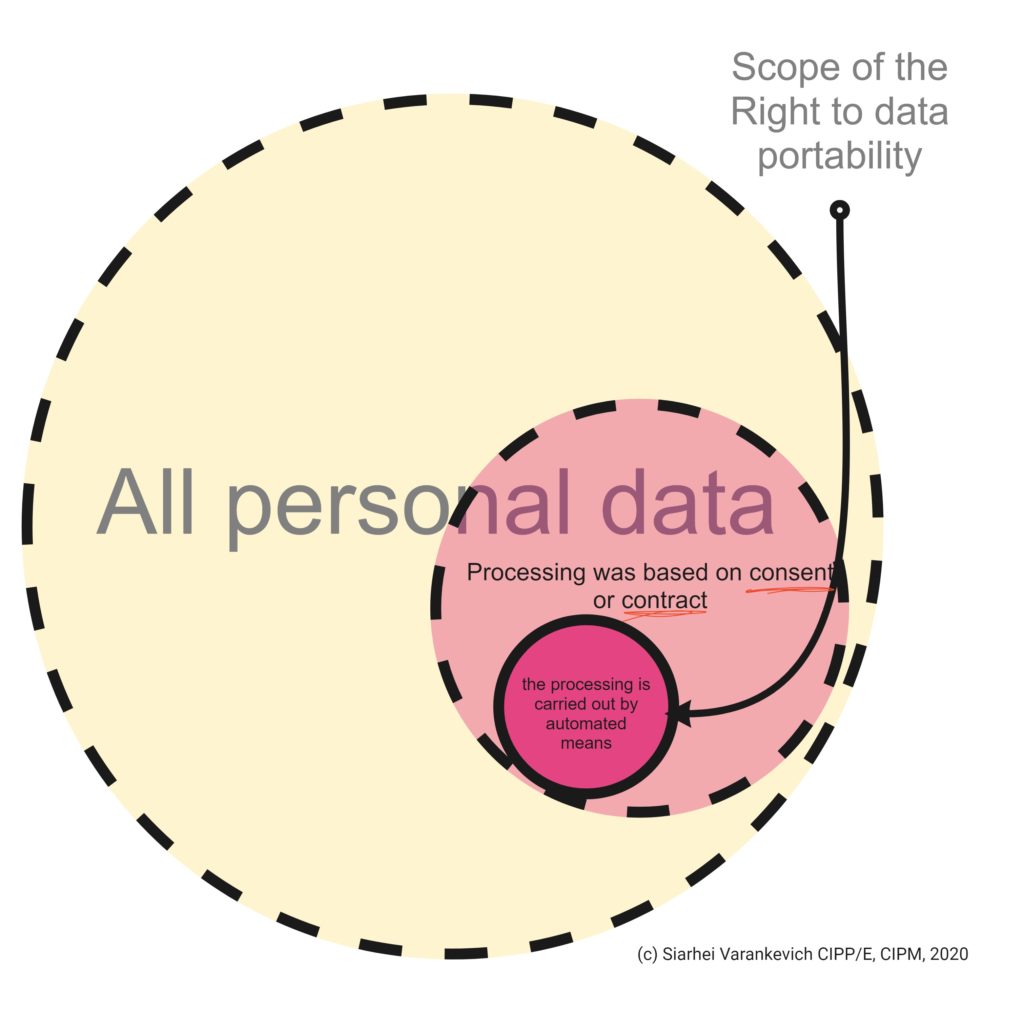






1. The data subject shall have the right to receive the personal data concerning him or her, which he or she has provided to a controller, in a structured, commonly used and machine-readable format and have the right to transmit those data to another controller without hindrance from the controller to which the personal data have been provided, where:







2. In exercising his or her right to data portability pursuant to paragraph 1, the data subject shall have the right to have the personal data transmitted directly from one controller to another, where technically feasible.
The latest consolidated version of the Regulation with corrections by Corrigendum, OJ L 127, 23.5.2018, p. 2 ((EU) 2016/679). Source: EUR-lex.
The right to data portability is presented primarily as a way to support “user choice, user control, and user empowerment” (Guidelines on the Right to Data Portability), as it aims at reinforcing an individual’s control over her/his personal information (recital 68). Data portability allows users to receive a copy of their personal data and can be seen in that sense as an extension of the right of access (article 15). It can also help them to switch services without losing their data, enabling users to transfer their information from one service to a potentially better one.
[…]
Sign in
to read the full text
Concern: Exercise my right to data portability
Dear Madam, Dear Sir,
I would like to exercise my right to data portability under Article 20 of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)…
[…]
Sign in
to read the full text
ISO/IEC 27701, adopted in 2019, added additional ISO/IEC 27002 guidance for PII controllers.
Here is the relevant paragraph to article 20 GDPR:
7.3.8 Providing copy of PII processed
Control
The organization should be able to provide a copy of the PII that is processed when requested by the PII principal.
Implementation guidance
The organization should provide a copy of the PII that is processed in a structured, commonly used, format accessible by the PII principal.
[…]
Sign in
to read the full text
(68) To further strengthen the control over his or her own data, where the processing of personal data is carried out by automated means, the data subject should also be allowed to receive personal data concerning him or her which he or she has provided to a controller in a structured, commonly used, machine-readable and interoperable format, and to transmit it to another controller. Data controllers should be encouraged to develop interoperable formats that enable data portability. That right should apply where the data subject provided the personal data on the basis of his or her consent or the processing is necessary for the performance of a contract. It should not apply where processing is based on a legal ground other than consent or contract. By its very nature, that right should not be exercised against controllers processing personal data in the exercise of their public duties. It should therefore not apply where the processing of the personal data is necessary for compliance with a legal obligation to which the controller is subject or for the performance of a task carried out in the public interest or in the exercise of an official authority vested in the controller. The data subject's right to transmit or receive personal data concerning him or her should not create an obligation for the controllers to adopt or maintain processing systems which are technically compatible. Where, in a certain set of personal data, more than one data subject is concerned, the right to receive the personal data should be without prejudice to the rights and freedoms of other data subjects in accordance with this Regulation. Furthermore, that right should not prejudice the right of the data subject to obtain the erasure of personal data and the limitations of that right as set out in this Regulation and should, in particular, not imply the erasure of personal data concerning the data subject which have been provided by him or her for the performance of a contract to the extent that and for as long as the personal data are necessary for the performance of that contract. Where technically feasible, the data subject should have the right to have the personal data transmitted directly from one controller to another.
Article 29 Working Party, Guidelines on the Right to Data Portability (2017).
Information Commissioner’s Office, Right of Access (2020).
EDPB, Guidelines 02/2021 on Virtual Voice Assistants (2021).